BS EN 1634-1 – Fire and Smoke Resistant Doors
European and British standardisation for fire-resistant hardware
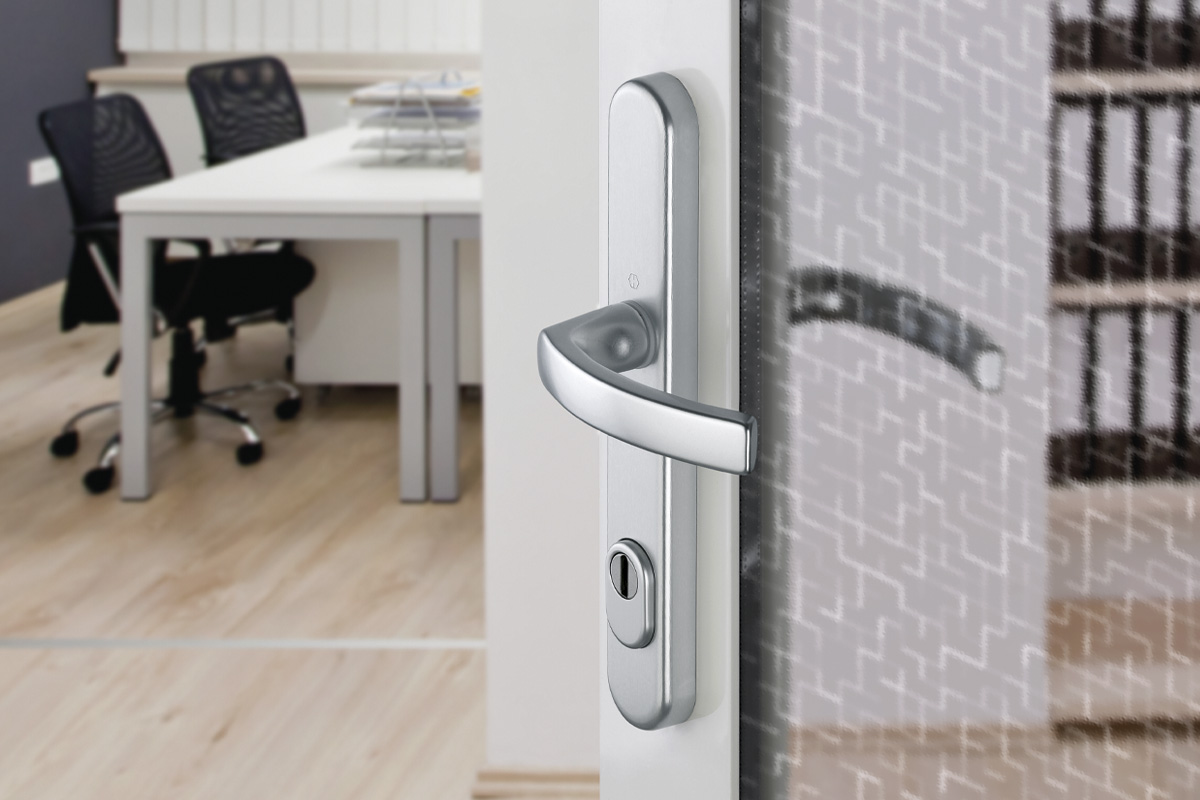
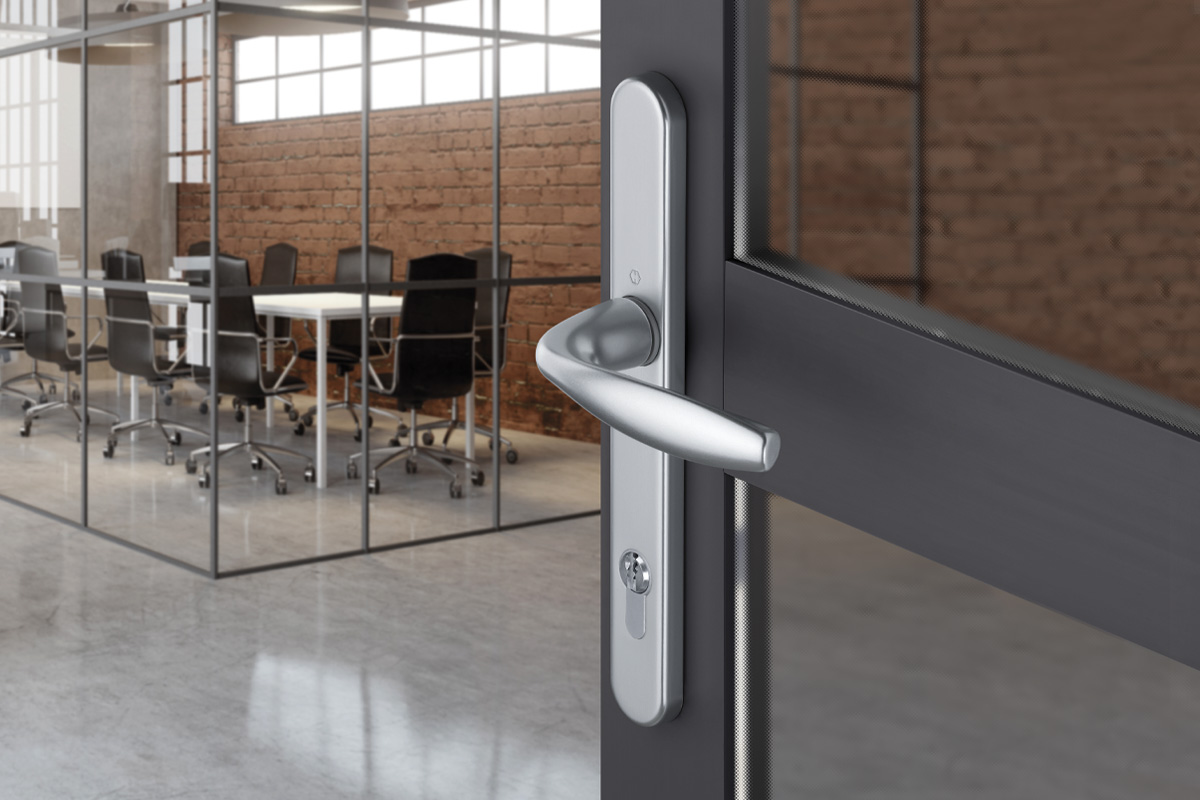
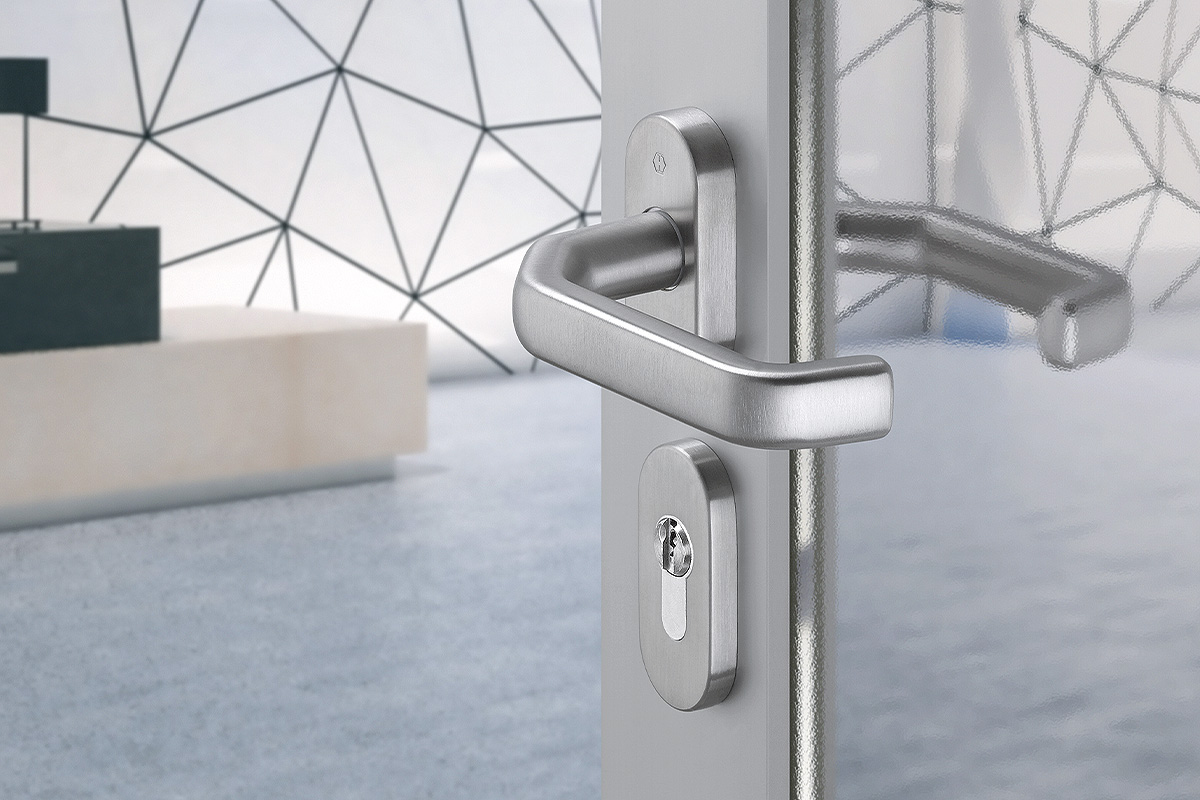
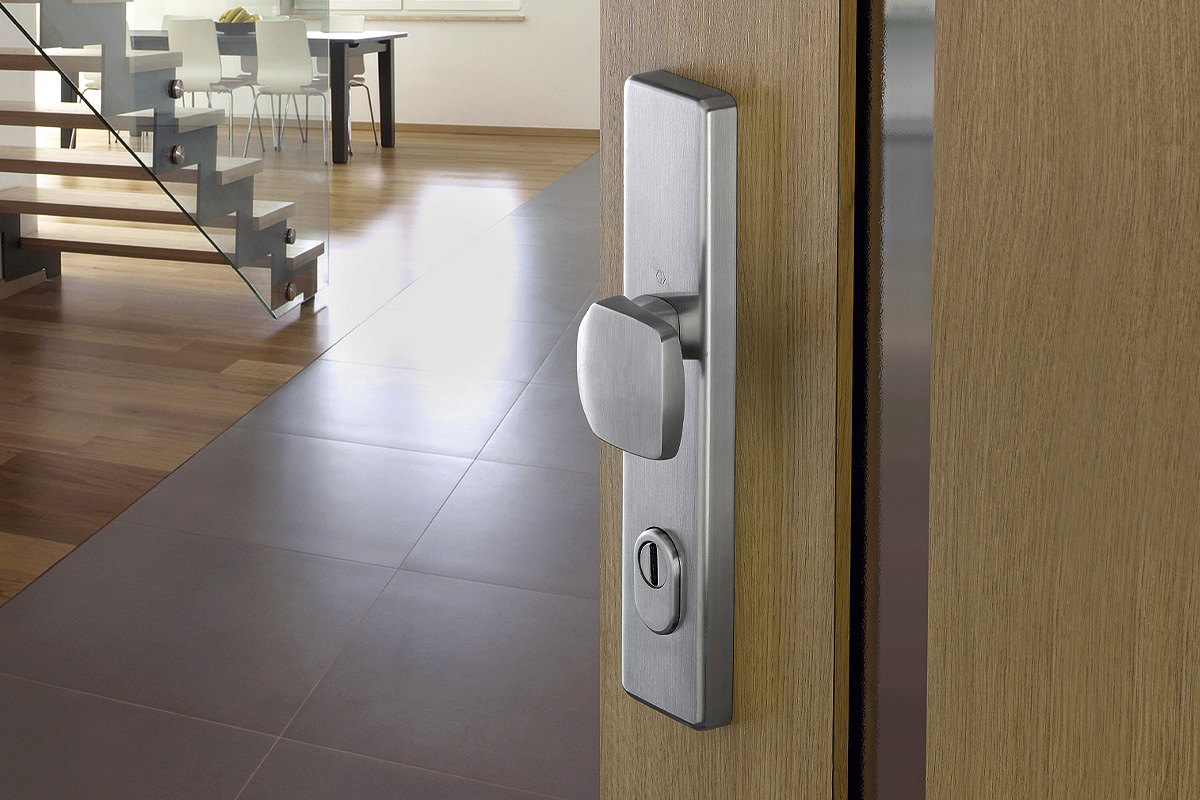
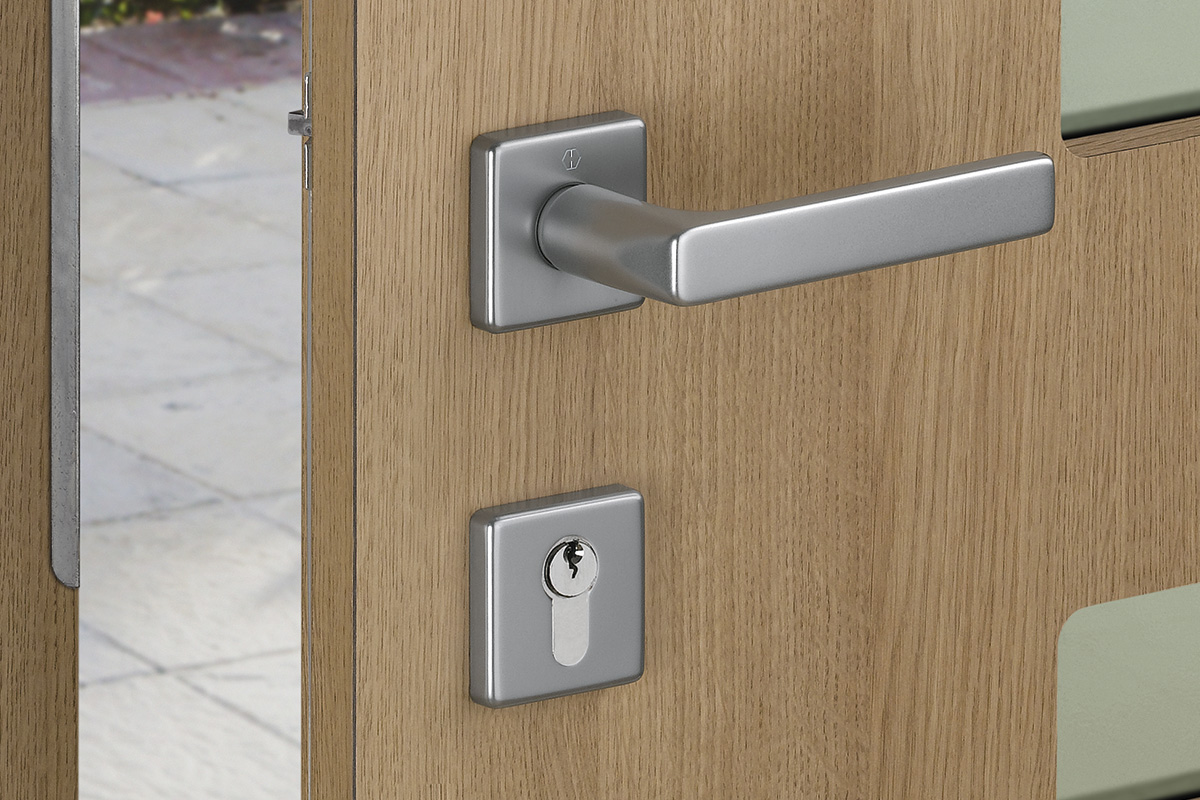
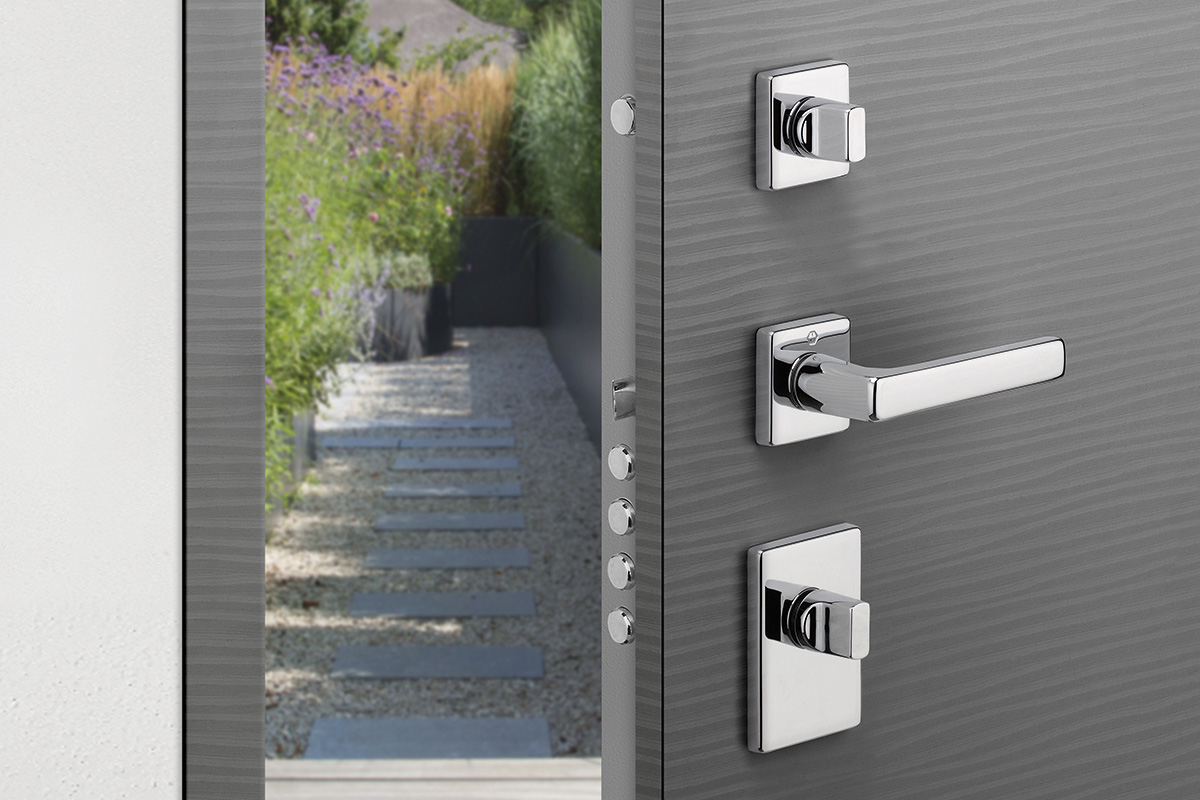
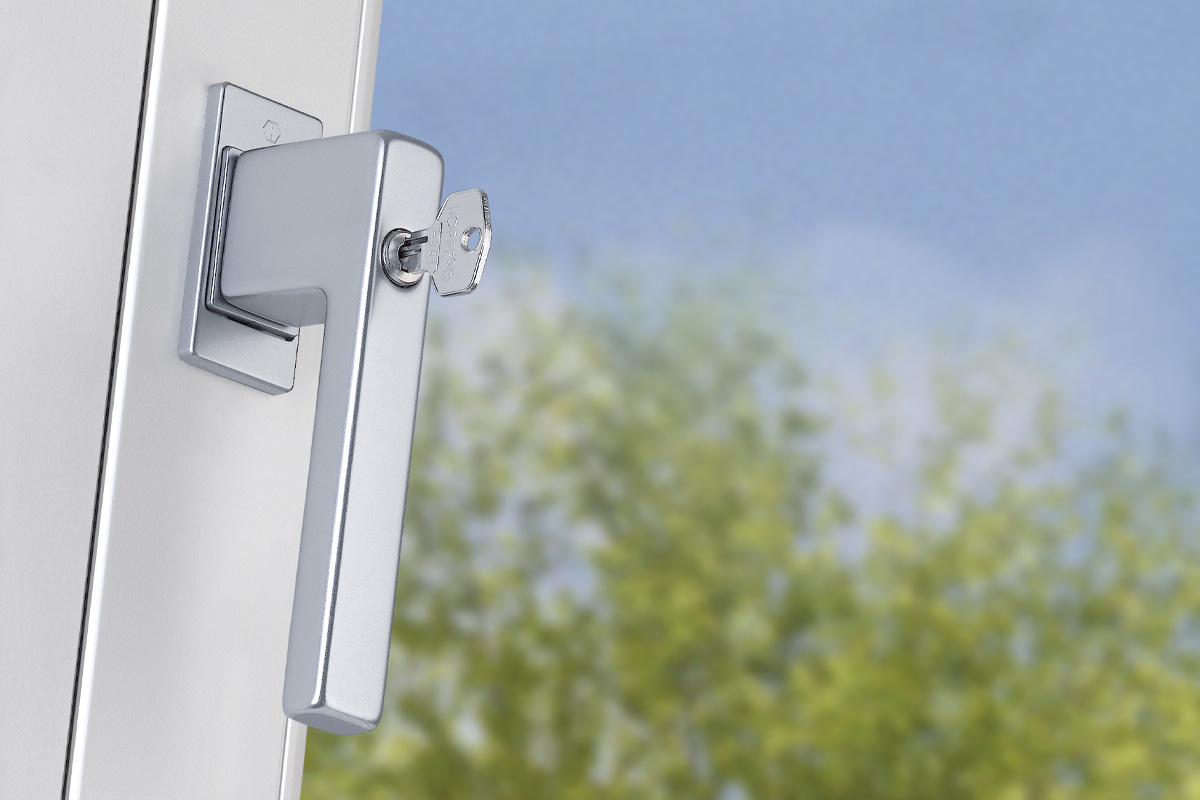
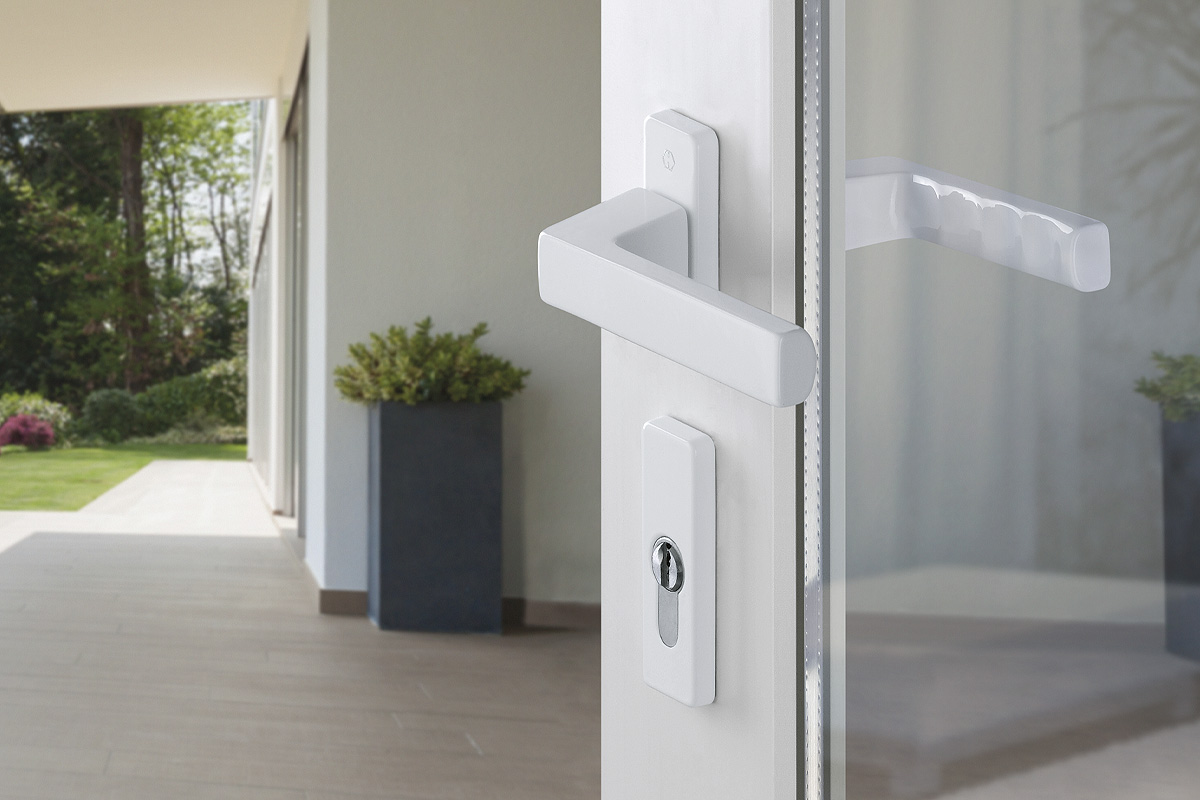
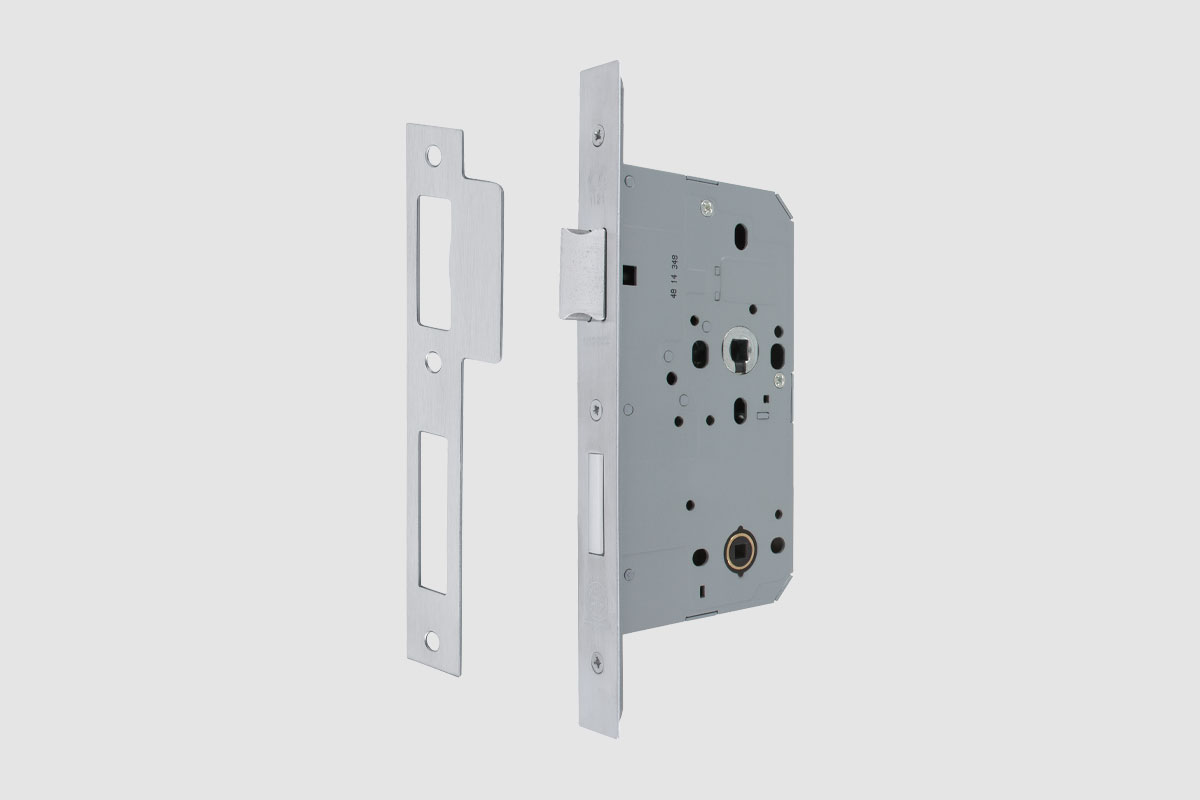
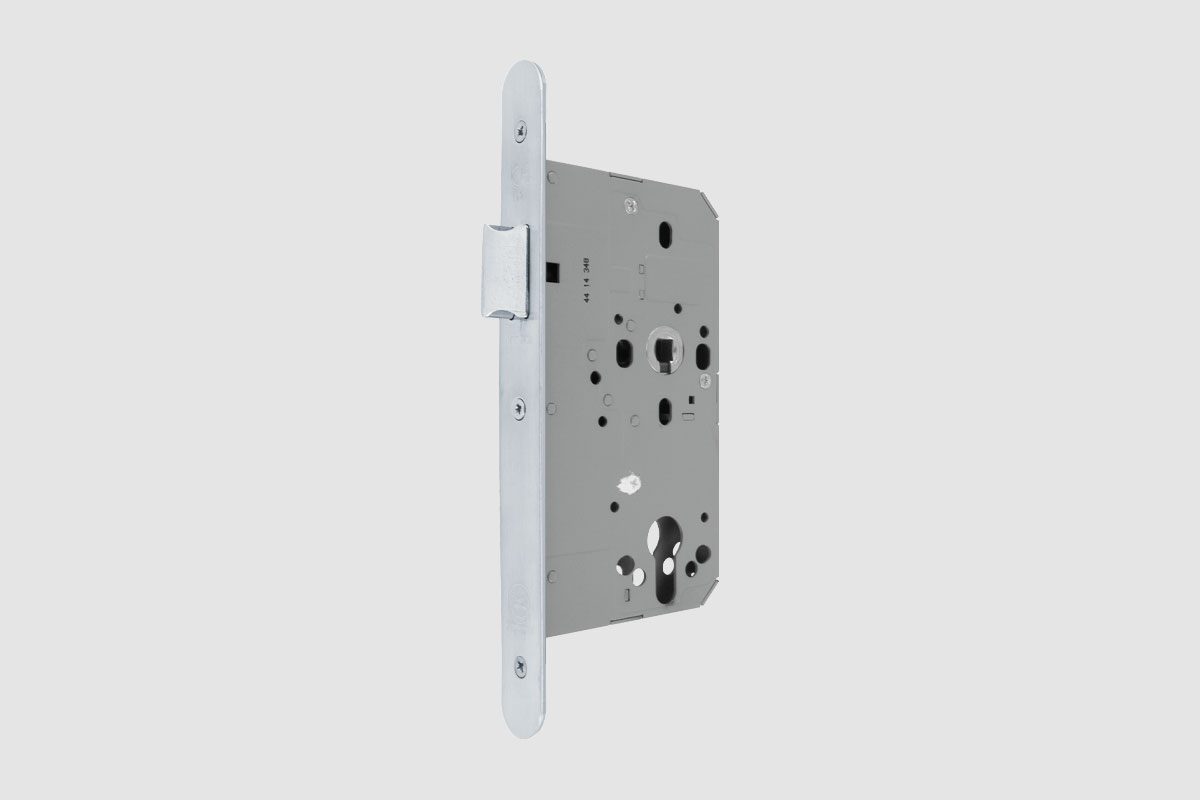
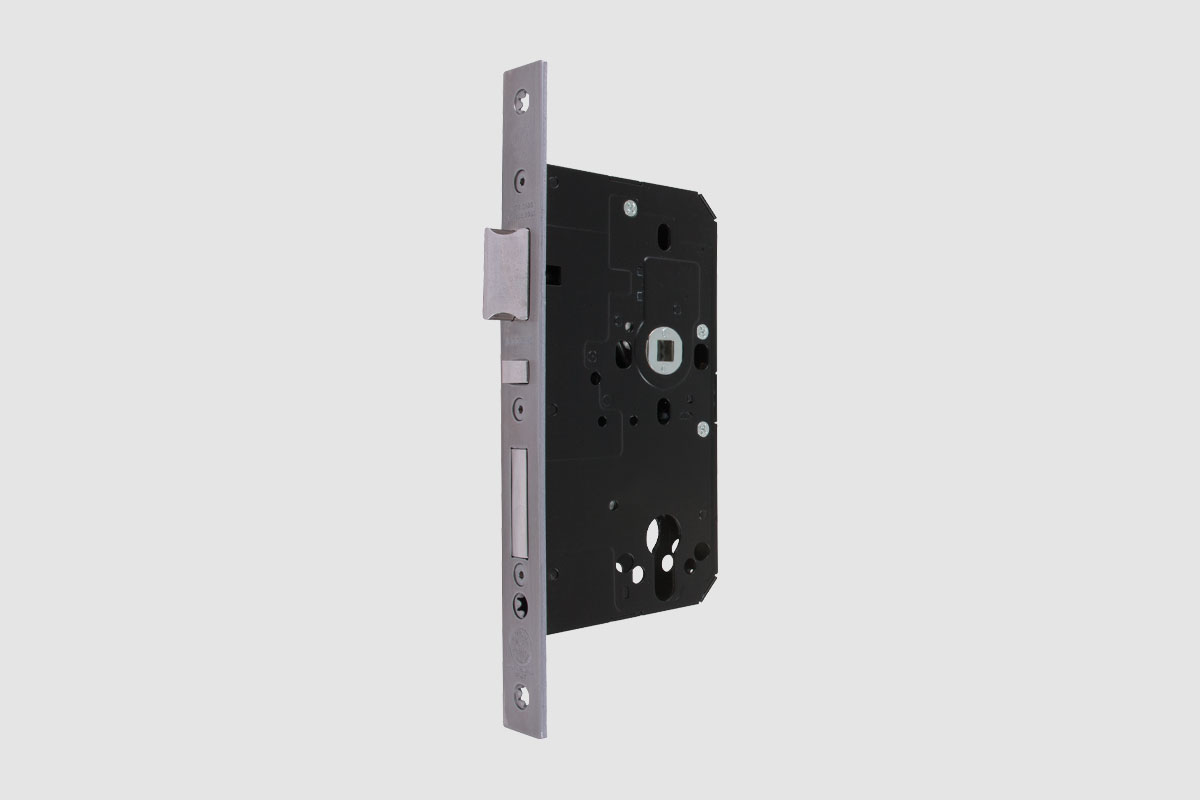
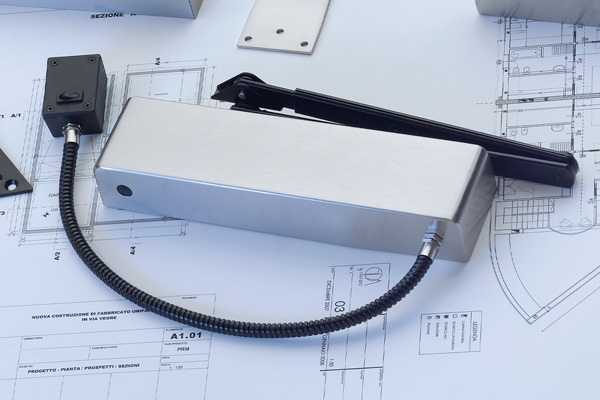
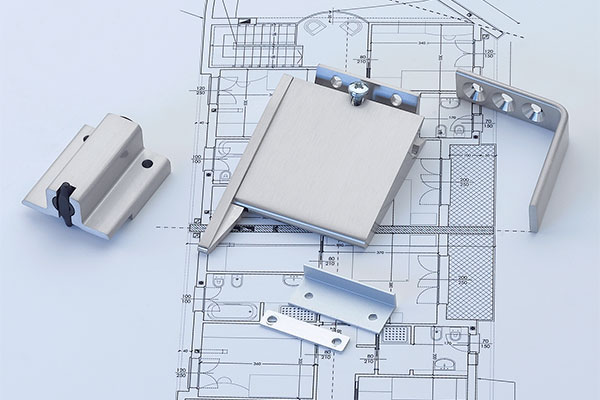
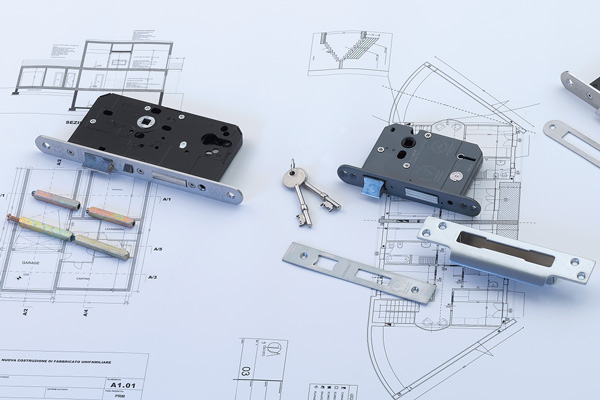
BS EN 1634-1:2014 + A1:2018 – Fire resistance tests for door and shutter assemblies
Fire-resisting doors serve three main purposes in a building:
- To restrict the initial development of a fire – A correctly fitted and functioning fire-resisting door can help to suppress a fire by restricting the amount of oxygen available to it.
- To restrict the spread of fire – A closed fire-resisting door is designed to endure direct attack by fire for a specified period of time. This should restrict the spread of fire through the building, gaining time for evacuation of the premises and for active fire protection resources such as sprinklers and fire fighters to perform their functions.
- To protect escape routes – The provision of protected escape routes is a requirement of Building Regulations. Any door opening on to an escape route or operating across an escape route is likely to be designated as a fire-resisting door, to ensure that persons using the route have protection from fire while they escape.
After evacuation, fire-resisting doors should continue to provide some protection for fire fighters entering the building to extinguish the fire.
Under BS EN 1634-1 test regimes, a door withstands fire attack for a period of time, for example 36 minutes or 67 minutes, and for the purposes of regulations is then described as E30, E60,
etc. (BS EN 1634-1). Withstanding fire attack means not allowing flames or hot gases to pass. In other words, the doorset maintains its fire integrity.
Classification:
By using this EN standard, the performance of building hardware for fire-resisting doors and emergency escape doors can be quantified in any or all the following areas:
- Category of use
- Durability
- Door size/mass
- Fire resistance
- Safety
- Corrosion resistance
- Security
All new European building hardware standards use a classification system in which the first seven digits are common. Each digit relates to a feature of the product measured against the requirements of the relevant standard. It is digit 4 that relates to the fire resistance of the product, they are graded as follows:
Fire resistance
Grade 0 – not approved for use on fire / smoke door assemblies
Grade A – suitable for smoke door assemblies – subject to test evidence
Grade B – suitable for fire and smoke door assemblies – based on a test in accordance with BS EN 1634-1
Source: Code of Practice: Hardware for Fire and Escape Doors – Issue 4 – November 2012 – Door and Hardware Federation (DHF)